Outdoor Piping Applications – Using the Proper Materials
With the availability of various types of pipes such as galvanized metal, flexible PEX tubing, and PVC, which are designed for different outdoor piping applications, choosing the right piping material can be overwhelming. You can execute an outdoor piping application successfully when you know the pros and cons of the various piping materials and understand which types suit specific applications. Here is a detailed breakdown of various outdoor applications and their corresponding piping materials.
Irrigation
Plastic irrigation piping materials revolutionized residential and commercial irrigation systems in the 1940s replacing copper water pipes, galvanized steel and asbestos cement cast-iron pipes. Farmers and building construction professionals started opting for plastic piping because it’s lightweight and its excellent corrosive resistance nature.
Types of Piping Materials used in Irrigation
Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe: PVC pipe is a durable thermoplastic pipe that is resistant to most chemicals. Although some contractors and designers use polyethylene (PE) and asbestos-cement for sub-mains, laterals, PVC is commonly used in most irrigation applications. The common standards available are Schedule 40 PVC pipe and Schedule 80 PVC pipe.
Cast-Iron Pipe: The piping material has been used for decades in most city water mains. However, the flow capacity of cast-iron diminishes with time. Therefore, there is a concern when it comes to clogging sprinkler orifices, especially after performing maintenance and repairs. The backfill after installation of this piping material should be free of rocks and debris.
Asbestos-Cement Pipe: The material is strong and free of rust and corrosion. It’s comprised of silica and is nonmetallic; it doesn’t conduct electricity and can resist galvanic action and electrolysis.
Copper Water Tubing: Many plumbing codes recommend the use of this material for the irrigation industry because it quickly tarnishes to blend with plant material and it doesn’t rust. It comes in three main types K, L and M that are designed for various irrigation applications. While K and L are available in both soft-annealed and rigid lengths for use in fewer irrigation applications, type M is suitable for turf irrigation systems because of its thick walls.
Polyethylene Pipe: The material should be installed with care because it’s weaker than its counterpart PVC. It has lower pressure ratings. In fact, these pipes can also slither in the trench and affect sprinkler placement during installation.
Underground wiring
There are different types of electrical conduits used for providing the route of electrical wiring. Many electrical conduits are made of plastic, metal or rigid fiber. The conduits have to be installed by electricians by following the regulations and standards of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Types of Underground Electrical Wiring Conduits
Galvanized Rigid Conduit: This is a conduit that is made from galvanized steel tubing. It is a thick rigid conduit that gives the electrical wiring maximum protection against threading and being hit. They are normally available in 10 and 20 feet and usually used in industrial and commercial applications. Also, different coatings can be applied to the conduit to prevent corrosion.
Electrical Metallic Tubing: Is either made of steel or aluminum and is often cheaper than galvanized rigid conduit. It is used for industrial and commercial underground wiring applications because it’s thinner and can be bent to specific radius and directions. It can also be used in residential projects because it has an excellent exterior corrosion resistance surface.
Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing: It is a moisture resistant and flame retardant material made of thin-walled corrugated tubing. It’s so flexible that it can be bent by hand during installation. Therefore, it’s suitable for lower labor cost and faster installations.
Aluminum Electrical Conduits: Is commonly used in commercial and industrial underground wiring applications, especially in water and corrosion-prone areas. It shouldn’t be embedded directly to concrete because it reacts with the alkalis in cement. However, it can be protected by applying certain protective coatings to its surface before installation.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Is the most common type in all electrical conduits because it’s affordable and lighter. These pipes vary in thickness, and thus a constructor has to determine the right type for a specific installation. The conduit effectively resists moisture and corrosion even though the tubing is non-conductive. Hence an extra grounding conductor should be passed into every conduit. However, mutual heating can cause complications on the cable performance when the conduit is installed underground in several parallel run configurations.
Pool Installation
Leaks are the most frustrating part of maintaining a pool. They are not only difficult to locate and fix, but also costly. However, using durable and high-quality pool piping materials is the most viable solution to managing a pool almost effortlessly.
Recommended Pool Piping Materials
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipes: There are two common types, namely rigid PVC pipes and flexible PVC pipes. Both types are similar regarding chemical makeup, solvents, tools, and fittings. The most recommended is schedule 40 as 20 would too thin, and schedule 80 pipes could be too thick for pool piping application.
CPVC Pipes: These pipes have a higher resistance against heat than PVC pipes. That is why they’re commonly used on pool heaters for inlet and outlet ports. They are suitable for commercial applications because it’s mandatory to use heat resistant pool piping materials. The recommended size is 36″ CPVC pipes for the inlet and outlet ports.
Polyethylene Pipes: These pipes were common for pool plumbing before PVC came along. The two main types of poly pipes are high density, and low density also called HDPE and LDPE respectfully.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) pipes: These materials are often used because of their affordability. However, their quality is quite low compared to the rest. They’re not ideal for the closed loop pressure found in pool plumbing systems.
Wells
Private wells that provide water for residential consumption ought to be well-maintained and kept safe at all times. Hence, the type of pipe used for this application is a major safety consideration. Most well designers and constructors prefer plastic pipes because they are not corroded by chemical treatments and minerals found in wells.
Recommended Types of Well Pipe Materials
PVC Pipe: The ends of these pipes are normally pre-threaded. Contractors use stainless steel couplings to make watertight connections. The pipe is resistant to sunlight and bleach. Remember, bleach is used for treating water wells.
Black Plastic Pipe: They come in schedule Thickness similar to that of PVC. However, these pipes can be purchased in rolls ranging from 100 to 1,000 feet. Stainless steel clamps are used to make watertight connections in special fittings.
Outdoor drainage
Different types of piping materials are used for different applications.
Types of Outdoor Drainage Pipes
Corrugated Single-Wall ADS piping: It’s recommended for flexible piping applications. It shouldn’t be installed where it can be easily crushed because it is not a very strong material. Also, it can become clogged so easily compared to pipes with smooth walls.
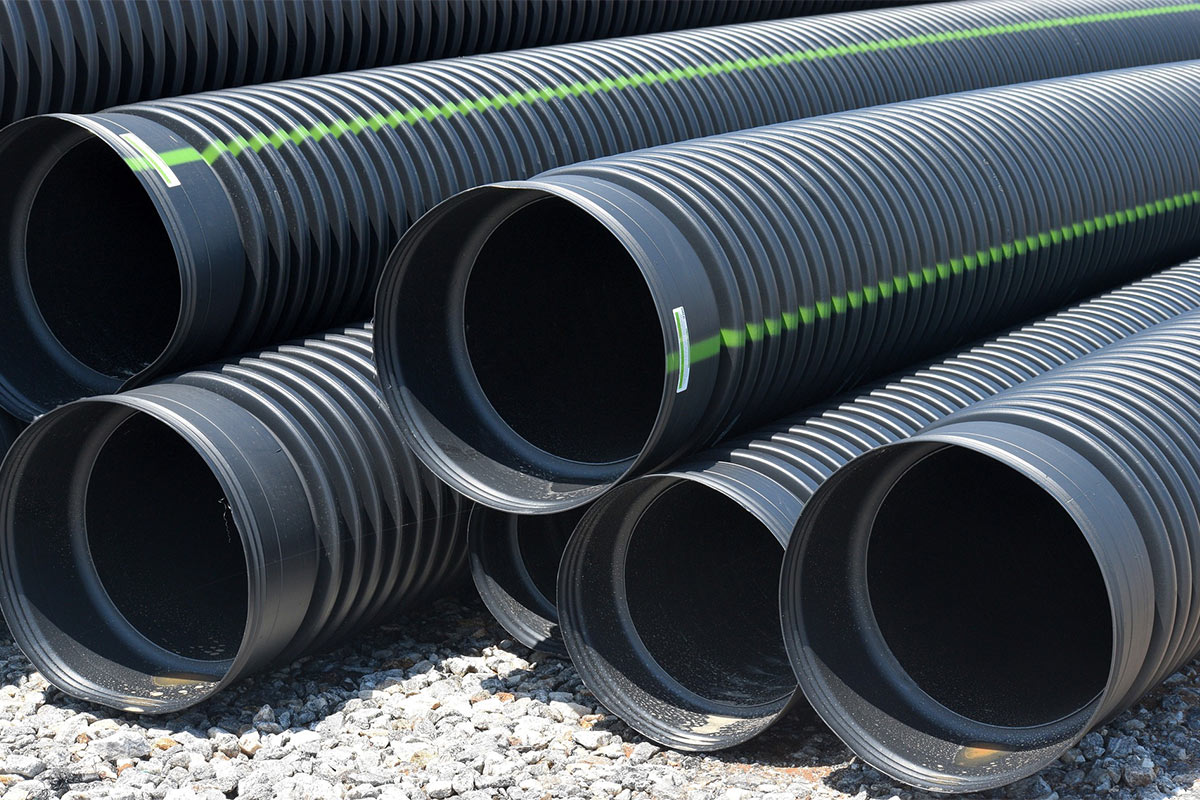
Double-Wall HDPE: It is a high-density piping material that is flexible yet more resistant to being crushed. The pipes are smooth on the inside but corrugated on the outside. The smooth inside allows for easier cleaning.
Sewer and Drain Pipe: It’s made of several layers of either PVC or polyethylene. Although the piping material has a smooth interior and exterior, it can be easily crushed.
Breakdown of Common Piping Materials recommended for Outdoor Applications
Schedule 40 vs. Schedule 80
The difference between the two is based on thickness, pressure rating, application, and color.
Thickness: The thickness of Schedule 40 PVC is thinner than that of Schedule 80 PVC pipes. However, both types have the same inside and outside diameters
Pressure rating: Schedule 80 PVC pipes can handle higher water pressure than Schedule 40 PVC fittings
Application: Schedule 40 PVC pipe is recommended for residential use while Schedule 80 PVC pipe is suitable for industrial and commercial piping applications
Color differences: The standard colors used by most manufacturers are white for Schedule 40 PVC pipes and grey for Schedule 80 PVC pipes.
Different piping materials are designed for various outdoor piping applications. This list of applications and types of piping materials should be a guide on what material to use for a particular application. So, regardless of the cost of the project, it’s prudent to choose the right pipes for a specific outdoor piping application.